Introduction
In today’s digital era, cloud migration has become a critical step for businesses aiming to leverage modern technology’s potential. Cloud migration involves transferring digital assets, services, databases, IT resources, and applications from on-premise hardware to the cloud—a network of servers hosted on the Internet. This transition is essential in the digital transformation journey, offering unparalleled opportunities for growth and innovation across various industries.

Identifying the Drivers for Cloud Migration
Several key factors are driving businesses towards cloud migration:
Scalability and Flexibility: The cloud provides an efficient way to scale operations, accommodating growth without significant upfront investments in physical hardware.
Cost Reduction: Migrating to the cloud helps shift from a capital expenditure model to an operational expenditure model, reducing upfront costs and achieving more predictable ongoing expenses.
Data Security and Compliance: Enhanced security features and compliance with regulations make the cloud a crucial choice for handling sensitive data.
Enhanced Collaboration and Remote Working: Cloud services enhance team collaboration, supporting remote work with easy access to data and applications from anywhere.
Technological Competitiveness: Agility and innovation, essential in today’s fast-paced technological landscape, are bolstered by cloud adoption.
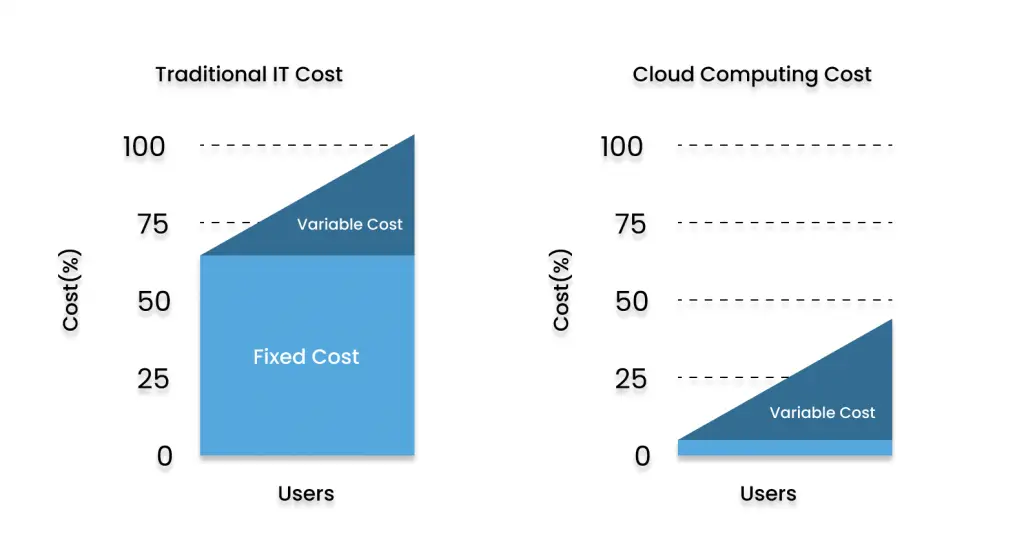
Total Cost of cloud computing deployments are approximately 1/3 of the traditional infrastructure
Challenges Faced Without Cloud Integration
Without cloud integration, traditional IT infrastructures present significant challenges:
Inefficiencies and High Maintenance Costs: Legacy systems require extensive maintenance, leading to inefficiencies and higher costs.
Limited Access and Collaboration Issues: Remote access and collaboration are hampered without the cloud, affecting productivity and flexibility.
Inadequate Disaster Recovery Solutions: Traditional systems often lack robust disaster recovery solutions, putting data at risk.
Scalability Challenges: Scaling operations with physical hardware is costly, time-consuming, and inflexible compared to cloud solutions.